Speak with our experts
Fill out our quick and easy contact form with your enquiry and we'll get back to you.
What are Bearings?
Pump bearings are a small, but essential part of pumps, as they carry the load of the pump and allow rotation.
Bearings are designed to minimise friction between turning parts on a fixed axis. They must be adequately lubricated, and temperatures monitored to prevent failure.
Bearings Explained
Why do Bearings fail?
Common Reasons for Bearing Failure
Improper Lubrication. The majority of bearing failures occur because of improper lubrication. Lubrication failure can occur if the wrong lubricant is used, if not enough or too much lubricant is applied, or if the bearing has been exposed to excessive temperatures that have caused the lubricant to degrade, (run out as liquid).
Corrosion & Contamination. Contaminants such as dirt, sand, water, and chemical compounds can cause numerous issues in bearing assemblies. For example, they can degrade the lubricant or corrode/erode bearing surfaces, all of which can lead to premature failure.
Bearings misalignment between the shaft and bearing housing, typical causes of misalignment.
Worn DE/NDEshield bearing housings.
Bent shafts contaminated components, and improperly positioned shafts and locking nuts. These issues can lead to uneven load distribution and excessive vibration generation, which can further hasten failure.
Fatigue—also referred to as spalling—refers to the fracture of bearing surfaces and the subsequent breaking off of pieces of material. As fatigue spreads, it will ultimately lead to failure.
Bearing Rating Life Calculation
How to calculate motor bearing life expectancy
Rating life is the bearing life calculated for 90% reliability. This is the amount of time that a group of apparently identical bearings will complete or exceed before the formation of a fatigue spall. The basic formula for calculating bearing L10 rating life is:
Note. This calculation is used for motor bearing.
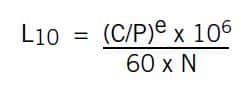
where:
C = Dynamic Capacity (dN or Lbs)
P = Equivalent Bearing Load (N or Lbs)
N = Rotating speed in RPM
What are the main types of Bearings?
1. Single Row Deep Groove Pump Bearings
These are most commonly used within the pump industry due to their mechanical advantages and manufacturing simplicity. They are non-separable and can be fitted with modifications to broaden their applications in pumps that carry different types of fluids. These bearings are primarily used to bear radial loads but can withstand axial loads.
2. Double Row Angular Contact Pump Bearings
Double Row Angular types as the name suggests have two rows of steel balls adjacent to each other.
Advantages:
- Performs at high RPMs.
- Can withstand both axial and radial loads.
- Low friction measurements
- Cheap manufacturing
Advantages:
- Endures high axial and radial loads together.
- Cheaper than two single row angular contact bearing.
- Takes up less room than two single row angular contact bearing.
- Quiet running noise.
- Allows tilting without damage or wear.
Disadvantages:
- Minimal impact load capacity
- Radial size can be larger compared to sliding bearings
Disadvantages:
- Installation requires more precision.
- Low impact load capacity
3. Universally Matchable Single Row Angular Contact Bearings
This type of bearing can handle high axial load in one direction. A universally matchable single-row angular contact bearing consists of one high and one low shoulder, which enables the bearing to accommodate many steel balls. Usually, these bearings are used in pairs to offset radial loads that often lead to unnecessary axial loads.
How to select the correct Bearing Change
We work closely with system designers to fully understand the application, in line with your specific requirements and ensure all your needs are met.
If you are experiencing frequent bearing wear this can often be a sign of a much larger issue, speak to our Pump expert at Pumpforce who can help you.
Advantages:
- High axial load bearing capacity.
- Handles quick acceleration and deceleration.
- Easy to match against a second bearing.
- Easy to install.
Disadvantages:
- Complex bearing housing design.
- High initial cost
Pump Bearings Maintenance
Maintenance Plans
We work with many customers, providing a maintenance package to ensure the pumps, controls and pressurisation units are working and operating at their most efficient.
You can view our pump maintenance and scheduling services here:
https://www.theforcegroup.co.uk/pump-force/pump-maintenance-scheduling-services
